Page 6 - PDF_Flip_Book
P. 6
Rod Machado’s Private/Commercial Pilot Handbook
2-26
Induced Drag
While some parasite drag is always present at slower speeds,
a different form of drag actually increases with a reduction in
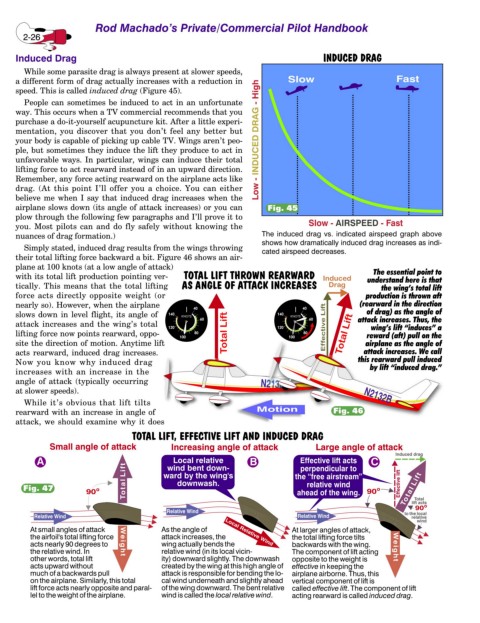
speed. This is called induced drag (Figure 45).
People can sometimes be induced to act in an unfortunate
way. This occurs when a TV commercial recommends that you
purchase a do-it-yourself acupuncture kit. After a little experi-
mentation, you discover that you don’t feel any better but
your body is capable of picking up cable TV. Wings aren’t peo-
ple, but sometimes they induce the lift they produce to act in
unfavorable ways. In particular, wings can induce their total
lifting force to act rearward instead of in an upward direction.
Remember, any force acting rearward on the airplane acts like
drag. (At this point I’ll offer you a choice. You can either
believe me when I say that induced drag increases when the
airplane slows down (its angle of attack increases) or you can Fig. 45
plow through the following few paragraphs and I’ll prove it to
you. Most pilots can and do fly safely without knowing the
nuances of drag formation.) The induced drag vs. indicated airspeed graph above
shows how dramatically induced drag increases as indi-
Simply stated, induced drag results from the wings throwing cated airspeed decreases.
their total lifting force backward a bit. Figure 46 shows an air-
plane at 100 knots (at a low angle of attack) The essential point to
with its total lift production pointing ver- understand here is that
tically. This means that the total lifting the wing’s total lift
force acts directly opposite weight (or production is thrown aft
nearly so). However, when the airplane (rearward in the direction
of drag) as the angle of
slows down in level flight, its angle of attack increases. Thus, the
attack increases and the wing’s total wing’s lift “induces” a
lifting force now points rearward, oppo- reward (aft) pull on the
site the direction of motion. Anytime lift airplane as the angle of
acts rearward, induced drag increases. attack increases. We call
Now you know why induced drag this rearward pull induced
by lift “induced drag.”
increases with an increase in the
angle of attack (typically occurring
at slower speeds).
While it’s obvious that lift tilts
rearward with an increase in angle of Fig. 46
attack, we should examine why it does
TOTAL LIFT, EFFECTIVE LIFT AND INDUCED DRAG
Small angle of attack Increasing angle of attack Large angle of attack
Induced drag
Local relative
A wind bent down- B Effective lift acts C
Total Lift ward by the wing's the “free airstream” Effective lift
perpendicular to
downwash.
relative wind
Fig. 47 o o Total Lift
90 ahead of the wing. 90 Total
lift acts
90 o
Relative Wind
Relative Wind Relative Wind to the local
relative
wind
At small angles of attack As the angle of Local Relative Wind At larger angles of attack,
the airfoil's total lifting force attack increases, the the total lifting force tilts
acts nearly 90 degrees to Weight wing actually bends the backwards with the wing. Weight
therelativewind. In relative wind (in its local vicin- The component of lift acting
other words, total lift ity) downward slightly. The downwash opposite to the weight is
acts upward without created by the wing at this high angle of effective in keeping the
much of a backwards pull attack is responsible for bending the lo- airplane airborne. Thus, this
on the airplane. Similarly, this total cal wind underneath and slightly ahead vertical component of lift is
lift force acts nearly opposite and paral- of the wing downward. The bent relative called effective lift . The component of lift
lel to the weight of the airplane. wind is called the local relative wind . acting rearward is called induced drag .